Artigo • 5 min read
Agentes de IA x chatbots de IA: entenda as diferenças
Agentes de IA e chatbots de IA são duas opções que as empresas podem usar para otimizar as operações e fornecer uma melhor experiência do cliente. Saiba qual é melhor para você abaixo.
Candace Marshall
Vice-presidente de marketing de produtos, IA e automação
A tecnologia de atendimento ao cliente percorreu um longo caminho desde os dias de música de espera infinita e “sua chamada é muito importante para nós”. Os avanços na inteligência artificial (IA) revolucionaram os processos de suporte ao cliente, tornando-os mais eficientes e intuitivos. À medida que as empresas aproveitam essas inovações, é importante distinguir entre duas ferramentas populares viabilizadas por IA: Agentes de IA vs. Os chatbots de IA
Esse detalhamento das diferenças entre um agente de IA e um chatbot de IA destacará como cada ferramenta funciona e onde cada uma se destaca. Entender essas distinções ajudará você a fazer investimentos que se alinhem melhor com suas metas de atendimento ao cliente e impulsionem um suporte mais eficaz.
Tópicos do guia:
- What is an AI chatbot?
- O que é um agente de IA?
- Diferenças entre um agente de IA e um chatbot de IA
- Como escolher entre um agente de IA e um chatbot de IA
- Perguntas frequentes
- Investa em um agente de IA líder do setor com a Zendesk
What is an AI chatbot?
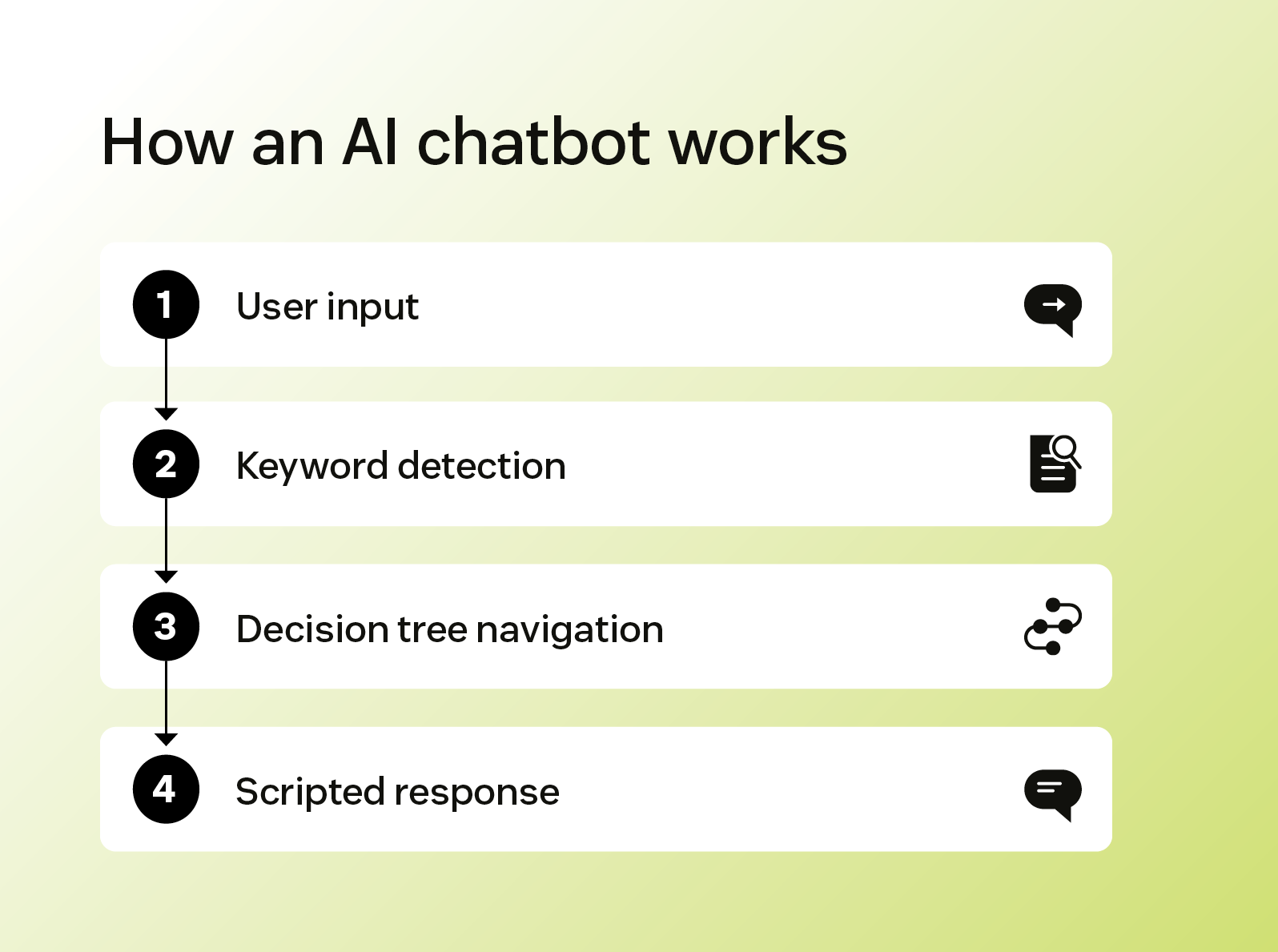
Um chatbot de IA é uma ferramenta que segue regras predefinidas para interagir com os clientes. Ele é programado para reconhecer palavras-chave em mensagens de clientes e responder com respostas com roteiros que orientam os usuários em um conjunto limitado de interações.
Esses sistemas dependem do processamento de linguagem natural (PLN) básico para identificar frases comuns e combiná-las com respostas predefinidas. Como resultado, eles não podem personalizar as respostas além do que é explicitamente programado.
Casos de uso de chatbot de IA
Os chatbots de IA são benéficos principalmente para gerenciar tarefas repetitivas que seguem padrões baseados em regras. Eles podem fornecer suporte automatizado para consultas comuns, simplificando a experiência do cliente.
Alguns casos de uso típicos incluem:
- Perguntas frequentes do cliente: Responder a perguntas comuns sobre itens como horário de funcionamento da loja, políticas de devolução ou configurações da conta
- Programação: Orientar os usuários ao agendar um compromisso ou uma reserva/li>
- Solução de problemas básicos: Orientar os clientes sobre soluções passo a passo para problemas conhecidos
Verificar status do pedido Acessar atualizações em tempo real de sistemas de back-end para compartilhar detalhes de remessa ou cronogramas de entrega
Um exemplo reconhecível é o chatbot de pedido de pizza da Domino, o “Dom”, que permite que os clientes façam um pedido e o acompanhem em tempo real. É uma maneira simples de manter os clientes informados sem entrar em contato com o suporte.
O que é um agente de IA?
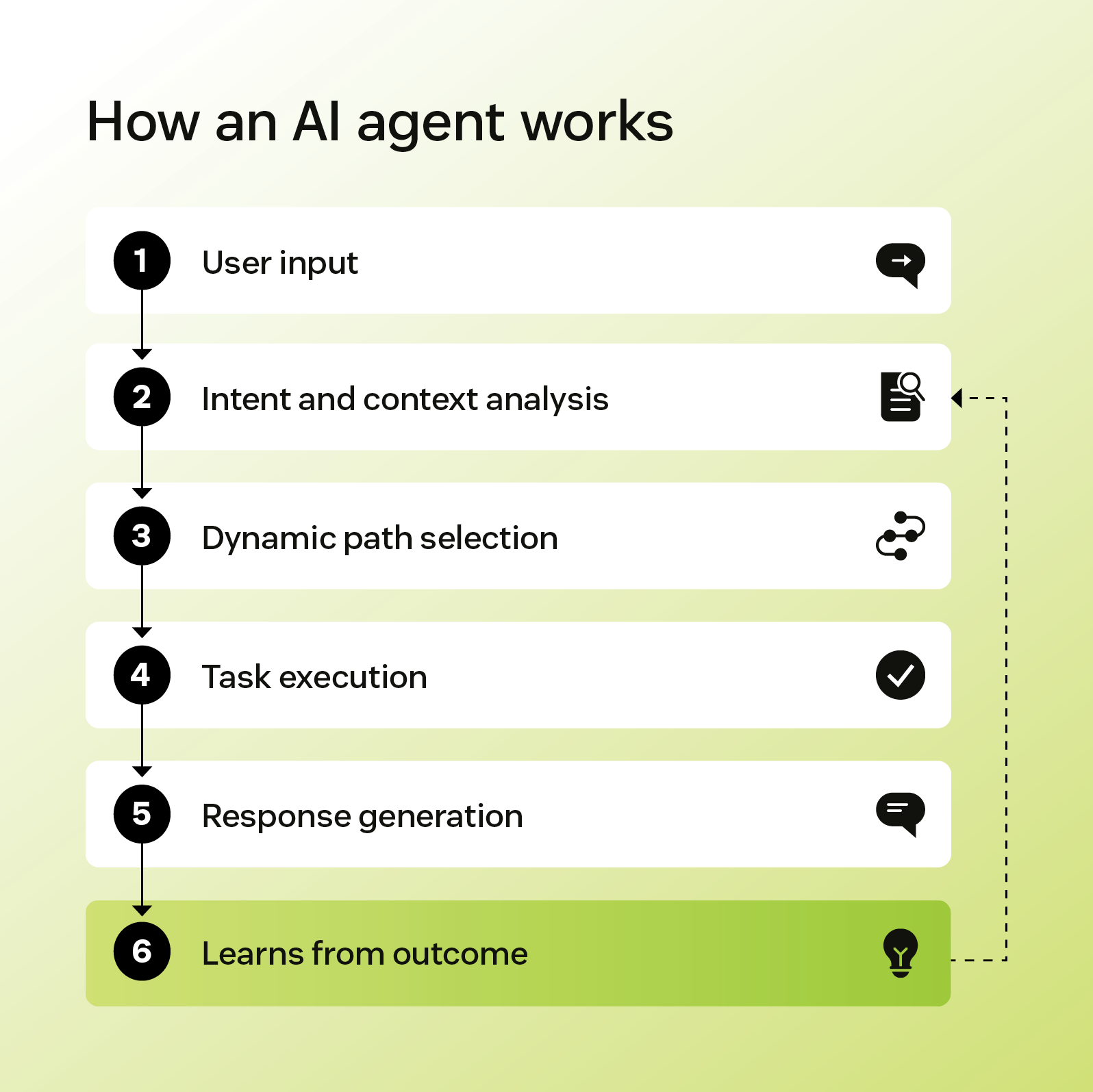
Um agente de IA é um programa autônomo que analisa conversas e toma decisões baseadas em contexto. Ao contrário dos chatbots, que seguem regras definidas, os agentes podem avaliar uma situação de forma independente, determinar o melhor curso de ação e executá-la.
Os agentes de IA são construídos em modelos de linguagem grande (LLMs), que permitem interpretar nuances e adaptar seu comportamento ao longo do tempo. Eles também podem se conectar a ferramentas externas, como sistemas de gerenciamento de relacionamento com o cliente (CRM), fornecendo informações que podem ser usadas para personalizar ainda mais as respostas ou concluir tarefas em nome de um usuário.
Casos de uso de agentes de IA
Como os agentes de IA podem realizar tarefas de forma independente, eles são usados principalmente para ajudar a resolver problemas mais complexos do cliente.
Alguns casos de uso específicos incluem:
- Resolução autônoma avançada: Resolver problemas de várias etapas, como disputas de faturamento ou remarcação de um voo sem intervenção humana
- Forneça suporte 24 horas por dia, 7 dias por semana: Ajudar os clientes a obter ajuda consistente, independentemente do fuso horário
- Tíquetes de encaminhamento: Avaliar conversas e encaminhar solicitações para a equipe certa ou nível de prioridade
Por exemplo, a Papier, empresa de papelaria com sede no Reino Unido, recorreu à Zendesk AI para apoiar sua expansão para os EUA. Agora, o agente de IA lida com um grande volume de solicitações após o expediente, ajudando a reduzir os acúmulos de tickets e melhorando os tempos de resposta em geral.
Diferenças entre um agente de IA e um chatbot de IA
Embora tanto os agentes de IA quanto os chatbots de IA sejam parte integrante do atendimento ao cliente moderno, eles diferem significativamente na forma como entendem e respondem às necessidades do cliente. Vamos dar uma olhada mais de perto em algumas das principais diferenças.
interação do atendimento ao cliente
Como os chatbots de IA seguem um roteiro, as interações tendem a parecer mais transacionais. Os clientes são guiados por um caminho definido com flexibilidade limitada, muitas vezes tendo que reformular ou reiniciar se sua pergunta não corresponder ao fluxo esperado.
Enquanto isso, as interações com agentes de IA se sentem mais conversacionais e personalizadas. Em alguns casos, os agentes podem até mesmo detectar possíveis problemas antes que um cliente entre em contato, permitindo suporte proativo em vez de apenas respostas reativas. Isso leva a uma experiência mais natural e satisfatória para os clientes.

Controle de qualidade
Os agentes de IA e os chatbots de IA desempenham um papel na garantia de qualidade (QA) coletando dados que esclarecem o desempenho dos agentes e a satisfação do cliente.
No entanto, os agentes de IA levam a perguntas e respostas adiante analisando conversas em tempo real e percebendo sutilezas como mudanças de sentimento e tom. Eles também podem gerar insights detalhados e alertar os supervisores imediatamente, permitindo intervenção e treinamento mais rápidos.
Os chatbots de IA, por outro lado, ajudam principalmente na coleta de feedback estruturado, como pesquisas de satisfação ou verificações simples de sentimento. Essa visão mais restrita se concentra nas reações do cliente em vez da dinâmica de conversa.
Complexidade da tarefa
Os chatbots de IA são limitados a lidar com tarefas simples com regras fixas e resultados previsíveis. Como eles seguem caminhos predefinidos, lutam com qualquer coisa que exija flexibilidade ou julgamento.
Em contraste, os agentes de IA estão equipados para gerenciar níveis mais altos de complexidade. Eles podem lidar com fluxos de trabalho de várias etapas, responder a mudanças no contexto durante a interação e tomar decisões com base em entradas em tempo real. Isso os torna mais bem equipados para resolver problemas de clientes diferenciados que os chatbots não conseguem resolver com uma única resposta por script.
Escopo do conhecimento
Os chatbots dependem de fontes de conhecimento predefinidas, portanto, seu escopo de conhecimento é limitado ao conteúdo para o qual foram treinados para fazer referência, como artigos da central de ajuda ou respostas roteirizadas. Se uma pergunta estiver fora desses limites, ela normalmente não pode fornecer uma resposta útil.
Os agentes de IA têm um escopo de conhecimento muito mais amplo porque podem acessar sistemas e ferramentas externas e usar LLMs para sintetizar informações relevantes em tempo real. Isso é especialmente valioso em setores como varejo, onde a IA pode acessar sistemas de estoque ou históricos de pedidos para fornecer respostas mais relevantes e precisas.
Aprendizagem e adaptabilidade
Os chatbots são amplamente estáticos, o que significa que não se adaptam ou melhoram de forma independente. Quaisquer atualizações exigem novo treinamento manual ou atualizações de regras por uma equipe humana. Por exemplo, se um chatbot continuar recebendo perguntas sobre um novo produto que não esteja em seus dados de treinamento, ele não poderá responder até que alguém adicione manualmente essas informações.
Os agentes de IA, por comparação, são criados para aprender com a experiência. Eles podem reter o contexto de conversas anteriores e ajustar o comportamento com base em novas informações. Ainda mais impressionantemente, eles podem aprender com os resultados, melhorando gradualmente a forma como respondem com base no que funcionou bem nas interações anteriores.
Como escolher entre um agente de IA e um chatbot de IA
À medida que a IA no atendimento ao cliente se torna mais comum, as empresas geralmente enfrentam uma decisão: Você precisa de uma ferramenta simples para automatizar perguntas de rotina ou de uma solução mais avançada para lidar com conversas e ações completas de forma autônoma?
A resposta depende de suas metas, recursos e do tipo de experiência que você deseja oferecer. Aqui estão alguns benefícios a serem considerados:
- Determine seu objetivo: Se você deseja automatizar interações diretas e acelerar os tempos de resposta, um chatbot pode ser suficiente. Mas se o seu objetivo for a resolução de ponta a ponta ou a personalização mais profunda, um agente de IA provavelmente será o mais adequado.
- Avalie seu orçamento: Os chatbots geralmente são mais econômicos de implementar e manter. No entanto, os agentes de IA podem oferecer maior valor a longo prazo, reduzindo os escalonamentos e economizando tempo em fluxos de trabalho mais complexos.
- Decidir qual é a experiência do cliente ideal: Pense no tipo de experiência que você deseja oferecer. A IA na experiência do cliente pode assumir muitas formas: os chatbots oferecem suporte rápido para necessidades previsíveis, enquanto os agentes de IA fornecem interações mais adaptáveis e personalizadas para clientes que precisam de assistência mais profunda.
- Pesar privacidade de dados: Como os agentes de IA acessam mais dados e sistemas, garanta que seu provedor priorize proteções de privacidade fortes e práticas de IA responsáveis.
É claro que essas ferramentas não são mutuamente exclusivas. Muitas empresas combinam chatbots e agentes de IA para fornecer suporte flexível em uma abordagem equilibrada.
Perguntas frequentes
História do cliente
[História do cliente:
Invista em um agente de IA líder do setor com a Zendesk
À medida que a IA reformula a experiência do cliente, os agentes de IA e os chatbots estão se tornando ferramentas indispensáveis para as empresas. Aproveitar essas ferramentas cuidadosamente pode permitir fluxos de trabalho mais eficientes que acompanhem as expectativas dos clientes.
Os agentes de IA da Zendesk oferecem resoluções instantâneas ininterruptas e reduzem os custos em escala. Treinados em bilhões de interações reais de atendimento ao cliente, eles se integram perfeitamente às suas operações de suporte e melhoram continuamente com base em dados em tempo real. Saiba mais sobre agentes de IA da Zendesk e o que eles podem fazer por sua empresa.
